CSS Validator User's Manual
Table of Contents
How to use the CSS Validator
The simplest way to check a document is to use the basic interface. In this page you will find three forms corresponding to three possibilities:
Validation by URL
Simply enter the URL of the document you want to validate. This document can be HTML or CSS one.
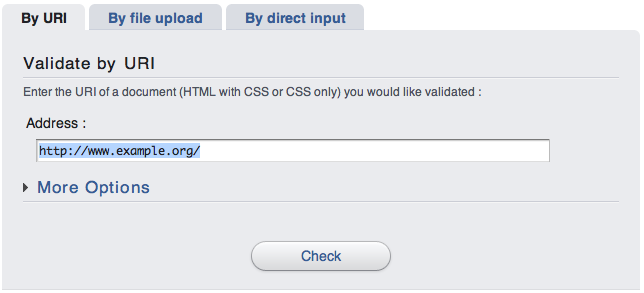
Validation by file upload
This solution allows you to upload and check a local file. Click the "Browse..." button and select the file you want to check.
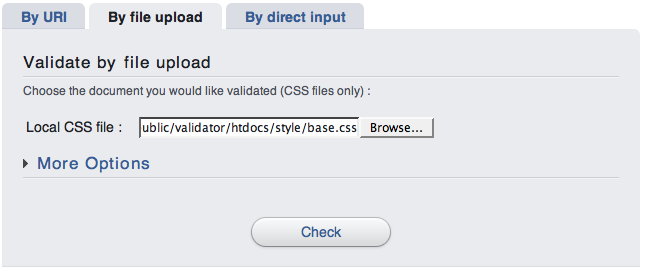
In this case, only CSS documents are allowed. It means that you cannot upload (X)HTML documents. You also must be careful with @import rules since they will be followed only if they explicitely reference a public URL (so, forget relative paths with this solution)
Validation by direct input
This method is perfect for testing CSS fragments. You just have to write your CSS in the textarea
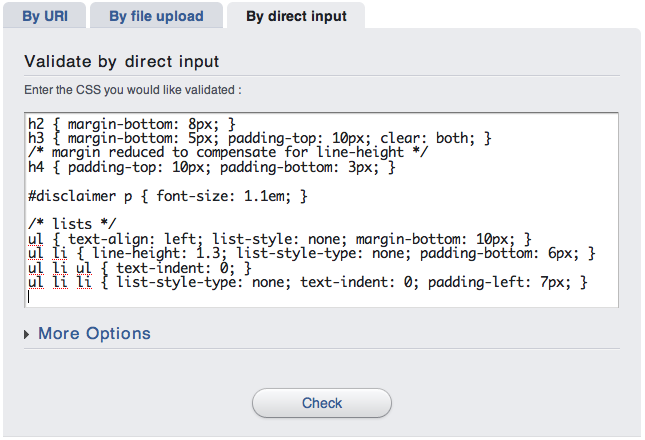
The same comments as before apply. Note that this solution is very convenient if you have a problem and need some help from the community. It's also very useful to report a bug, since you can link to the resulting URL to give a test case.
What does the basic validation do?
When using the basic interface, the validator will check the compliance
against CSS 2.1, which is the current
CSS technical recommendation.
It will produce an XHTML output without any warning (you will only see
errors).
The medium is set to "all", which is the medium suitable for all devices
(see
http://www.w3.org/TR/CSS2/media.html for a complete description of
media).
Advanced validation
If you need a more specific check, you can use the advanced interface which allows to specify three parameters. Here is a little help on each of these parameters.
Warnings
This parameter is useful to tune the verbosity of the CSS Validator. Indeed, The validator can give you two types of messages: errors and warnings. Errors are given when the checked CSS does not respect the CSS recommendation. Warnings are different from errors since they do not state a problem regarding the specification. They are here to warn (!) the CSS developper that some points might be dangerous and could lead to a strange behaviour on some user agents.
A typical warning concerns font-family: if you do not provide a generic font, you will get a warning saying that you should add one at the end of the rule, otherwise a user agent that doesn't know any of the other fonts will switch to it's default one, which may result in strange display.
Profile
The CSS validator can check different CSS profiles. A profile lists all the features that an implementation on a particular platform is expected to implement. This definition is taken from the CSS site . The default choice corresponds to the current most used one: CSS 2.
Medium
The medium parameter is the equivalent of the @media rule, applying to all the document. You will find more information about media at http://www.w3.org/TR/CSS2/media.html .
Experts Only
Validation Request Format
Below is a table of the parameters you can use to send a query to the W3C CSS Validator.
If you want to use W3C's public validation server, use the parameters
below in conjunction with the following base URI:
http://jigsaw.w3.org/css-validator/validator
replace with the address of your own server if you want to call a private
instance of the validator.
Note: If you wish to call the validator programmatically
for a batch of documents, please make sure that your script will
sleep for at least 1 second between requests.
The CSS Validation service is a free, public service for all, your respect is
appreciated. thanks.
| Parameter | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
| uri | The URL of the document to validate. CSS and HTML documents are allowed. | None, but either this parameter, or text must be
given. |
| text | The document to validate, only CSS is allowed. | None, but either this parameter, or uri must be
given. |
| usermedium | The medium used
for the validation, like screen,
print, braille... |
all |
| output | Triggers the various outputs formats of the validator. Possible
formats are
text/html and html (XHTML document,
Content-Type: text/html),
application/xhtml+xml and xhtml (XHTML
document, Content-Type: application/xhtml+xml),
application/soap+xml and soap12 (SOAP 1.2
document, Content-Type: application/soap+xml),
text/plain and text (text document,
Content-Type: text/plain),
everything else (XHTML document, Content-Type: text/html)
|
html |
| profile | The CSS profile used for the validation. It can be
css1, css2, css21,
css3, svg, svgbasic,
svgtiny, mobile, atsc-tv,
tv or none |
the most recent W3C Recommendation: CSS 2 |
| lang | The language used for the response, currently, en,
fr, it, ko, ja, es,
zh-cn, nl, de, it,
pl. |
English (en). |
| warning | The warning level, no for no warnings, 0
for less warnings, 1or 2 for more warnings
|
2 |
CSS Validator Web Service API: SOAP 1.2 validation interface documentation
For more technical help, in particular about the SOAP 1.2 output and all the possible ways to call the validator, see the CSS Validator Web Service API.

